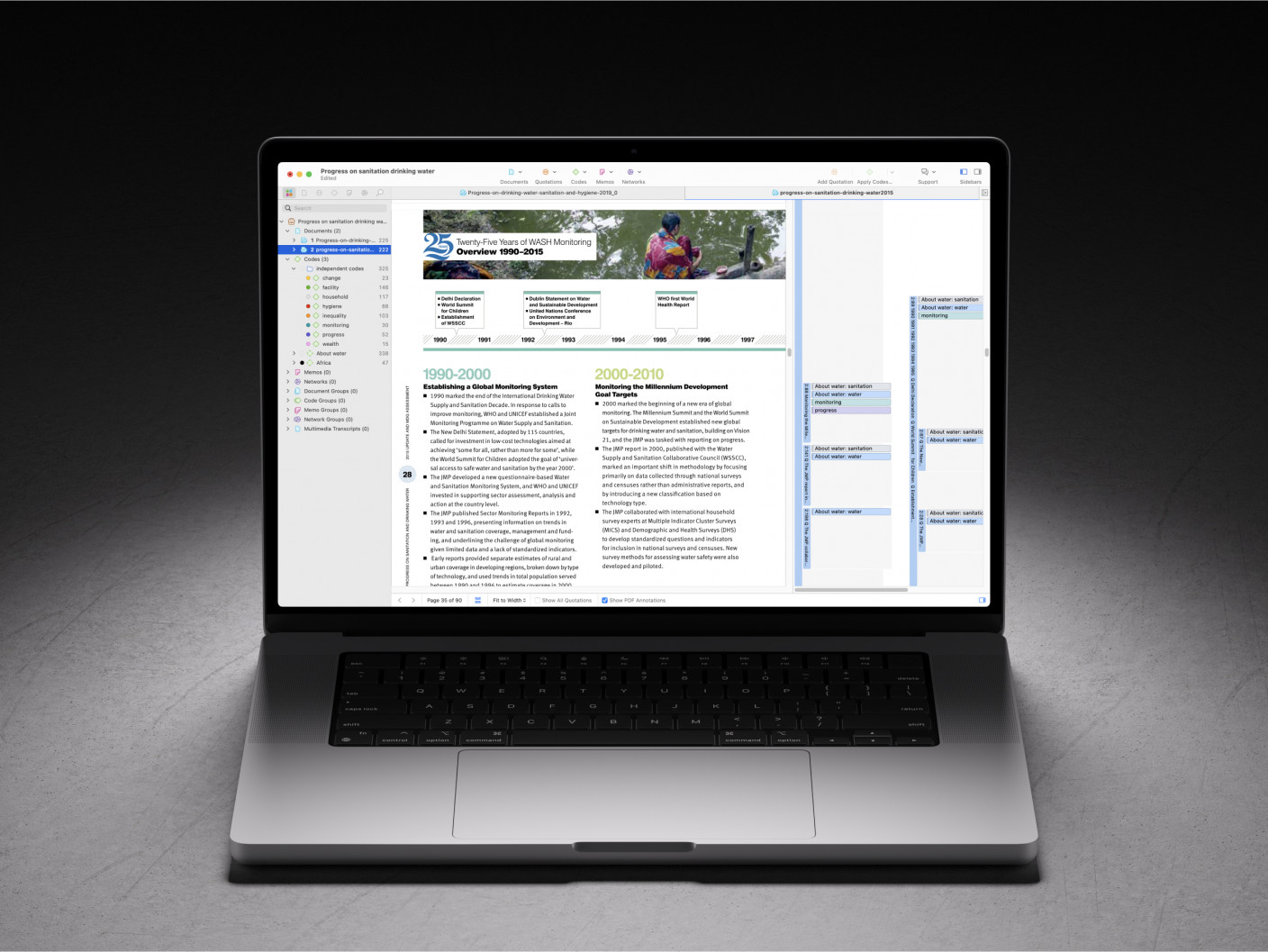
Why do qualitative researchers need thematic analysis?
Thematic analysis offers qualitative researchers a flexible yet systematic approach for examining data. This method is not tied to any specific theoretical framework, allowing researchers to apply it across a wide range of epistemologies and research questions. Here are several reasons why thematic analysis is indispensable for qualitative researchers:
- Versatility: It can be used with various data types, including interview transcripts, survey responses, and social media content, making it applicable to many research fields.
- Depth of insight: Thematic analysis allows researchers to examine the complexities and nuances of their data, providing a rich, detailed, and complex account of their findings.
- Accessibility: The process is accessible to researchers at different levels of experience, from beginners to experts, due to its clear and systematic nature.
- Transparency: By providing a structured approach to data analysis, thematic analysis enhances the transparency of qualitative research. Researchers can clearly demonstrate how their findings are derived from the data, which contributes to the credibility and trustworthiness of the research.
- Comprehensiveness: It enables researchers to examine large volumes of data in a manageable way, ensuring that potential insights are not overlooked.
What’s unique about thematic analysis?
Advantages with conducting thematic analysis center on its ease of use. In particular, thematic analysis is flexible, accessible, and can be applied to many different fields. When compared to other qualitative methods such as discourse analysis, narrative analysis, and content analysis, thematic analysis offers distinct advantages and features that cater to a wide range of research needs and questions.
Discourse analysis
Discourse analysis focuses on the way language is used in texts and conversations to construct meanings and social realities. It pays close attention to the context in which language is used and how power relations and identities are constructed through discourse. In contrast, thematic analysis takes a broader view of the data beyond (but including) language and discourse. This makes thematic analysis more versatile and applicable to a broader variety of data types, not just textual or conversational data.
Narrative analysis
Narrative analysis looks into the storytelling aspects of data, exploring how individuals construct and convey their experiences and realities through narratives. This approach is particularly focused on the structure and function of stories within the data, examining how these narratives help individuals make sense of their world. Thematic analysis, by contrast, is less concerned with the form or structure of narratives and more focused on identifying and analyzing themes that cut across the data, regardless of how they are narrated.
Content analysis
Content analysis is a method that quantifies content in terms of predetermined categories and often involves counting the frequency of words, themes, or concepts within the data. While content analysis provides a systematic way to analyze textual data, it tends to focus more on surface-level aspects of the data and less interpretative analyses compared to thematic analysis. Thematic analysis goes beyond mere counting or categorization to interpret the underlying ideas, assumptions, and conceptualizations within the data.