Best Practices for Writing the Introduction Section
The Introduction Section
Purpose
The Introduction should provide essential background information and clearly highlight the research gap that the paper aims to address. A well-crafted Introduction captures the interest of a wider audience, establishes relevance, and lays a solid foundation for understanding the study’s objectives. It sets the tone for the entire paper and ensures that the research is positioned well within the broader academic field.
Key Components of the Introduction Section
- Context or Background
Introduce the broader research area and highlight the significance of the subject of interest. - Current Knowledge in the Field
Summarize existing research, providing an overview of established knowledge in the field. - Gaps and Unanswered Questions
Identify unresolved questions or limitations in previous studies. This helps set the novelty of the study - Study Objectives and Research Questions
Mention the research problem, objectives, and the hypotheses being tested. - Importance of the Study
Explain why the research is relevant and what contributions it aims to make in the field.
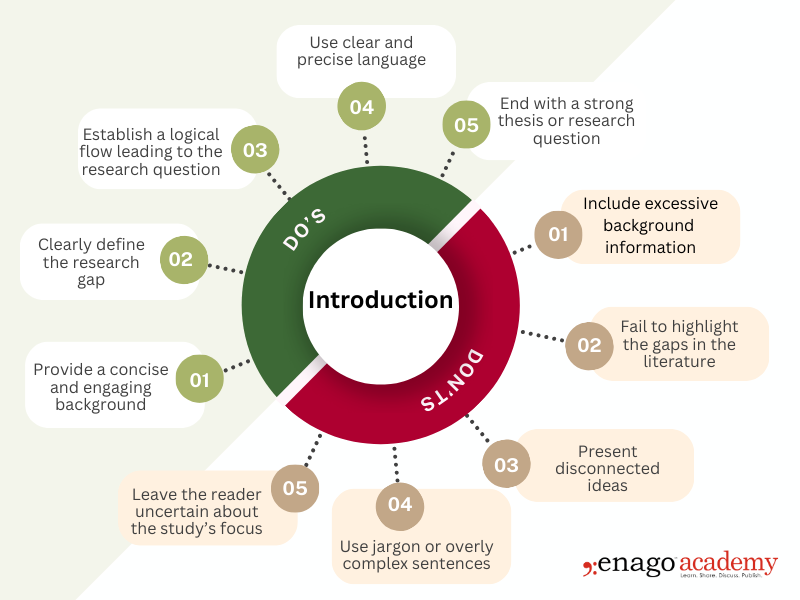 A well-structured Introduction section maintains the reader’s interest while ensuring that the research is properly contextualized. By keeping it concise and logically structured, authors can create a compelling entry point for their work.
A well-structured Introduction section maintains the reader’s interest while ensuring that the research is properly contextualized. By keeping it concise and logically structured, authors can create a compelling entry point for their work.
Ask yourself the following questions while you are working on the Introduction section of your research article:
- What is the broader topic of the research? Why is this topic important in the field?
- What is already known about this topic? What are the key studies and existing knowledge related to the research area?
- What are the gaps in current research? What is missing, unclear, or unresolved in previous studies?
- What does this study aim to investigate, test, or explore?
- What new insights, perspectives, or advancements does this research bring?
- What general methods or frameworks are being used?
The Discussion Section
Purpose
The Discussion should interpret and clearly state the implications of the findings. It should contextualize the results within field, acknowledge any limitations of the study, and propose directions for future research. Unlike the Introduction which sets up the research questions, the Discussion addresses how the findings answer those questions and what their broader significance is.
Key Components of the Discussion Section
- Summary of Key Findings
Summarize the important results that forms the foundation of the research paper - Comparison with Existing Research
Contextualize the findings by comparing them with previous studies, highlighting agreements and discrepancies. - Alternative Explanations
Discuss the implications and provide possible reasons for contradictory results. At times, this could be due to change in the model systems, methodology adopted, parameters analysed, etc. - Study Limitations
Acknowledge methodological constraints and other limitations. Do not overstate the findings. - Implications and Future Directions
Emphasize how the findings contribute to the field and propose potential avenues for future research. - Practical Applications
Discuss how the findings can be applied in real-world scenarios (if applicable).