Why rely on software for data analysis?
Why rely on software for data analysis?
Data analysis software offers several advantages that make it a valuable tool for researchers and professionals across various fields. These benefits can be categorized into three main areas: efficiency, accuracy, and capability.
Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of using data analysis software is the efficiency it brings to the data analysis process. Manual data analysis can be time-consuming, especially when dealing with large datasets or complex analyses. Data analysis software automates many of the tasks involved, such as data cleaning, organization, and calculation.
This automation reduces the time and effort required to perform these tasks, allowing users to focus on interpreting the results rather than getting bogged down in the mechanics of data handling. Additionally, the software can process large volumes of data much faster than manual methods, enabling users to complete their analyses in a fraction of the time it would take otherwise.
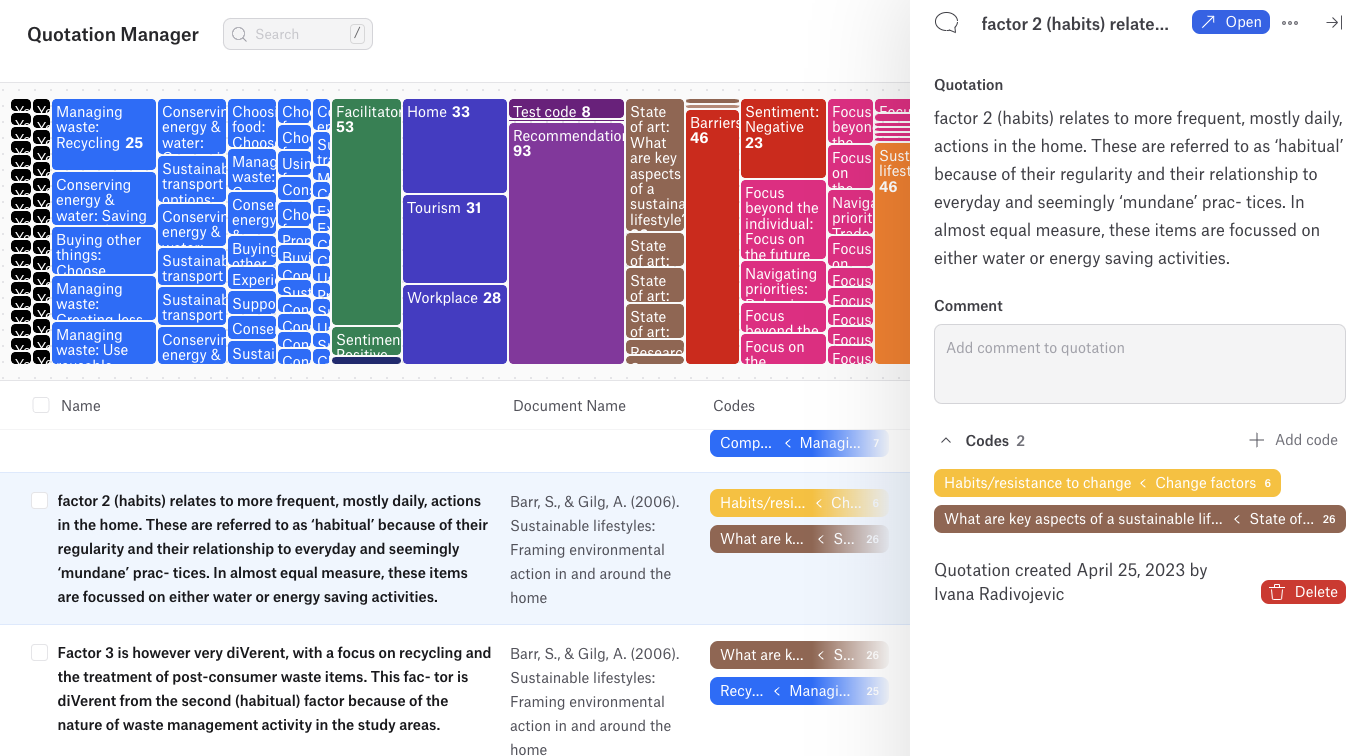
Accuracy
Accuracy is another benefit of relying on software for data analysis. Human error is a common issue in manual data analysis, particularly when working with large datasets or performing complex calculations.
Data analysis software minimizes the risk of such errors by automating the analysis process and providing tools that ensure consistency and precision. The software is designed to handle various types of data and perform calculations with high accuracy, reducing the likelihood of mistakes that could skew the results. Moreover, many data analysis programs include features that help identify and correct errors in the data before analysis begins, further enhancing the credibility of the results.

Capability
Data analysis software also expands the range of analyses that can be performed. While manual methods may be limited by the analyst’s skills and available time, software tools can handle a broader spectrum of analytical tasks. This includes advanced statistical analyses, data modeling, predictive analytics, and even machine learning algorithms.
These capabilities allow users to explore their data in more depth and uncover insights that might not be accessible through manual analysis. Additionally, many software programs offer data visualization tools that help users present their findings in a clear and impactful way, making it easier to communicate results to others.